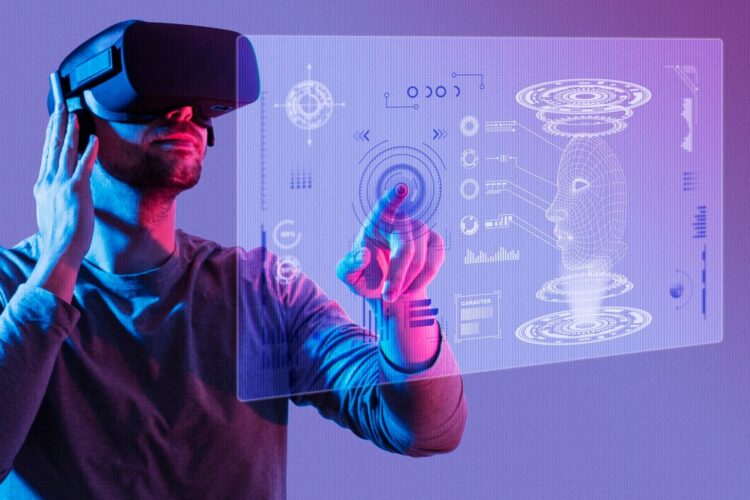
Immersive technologies, like augmented, virtual, and mixed reality, have grown incredibly fast over the last few years. What earlier felt like something out of a science fiction movie, or at least some sort of an experimental gadget, has now turned into real-world solutions applied in schools, offices, and even homes. The combination of more affordable devices and increasingly intuitive software is helping these tools move from niche to mainstream use. Thus, they are gradually changing how people learn, collaborate, and experience digital content in everyday life.
Immersive Learning in Education

These emerging technologies make classrooms in the education sector more dynamic than ever. Many schools and universities use VR headsets to take their students on virtual field trips to ancient civilizations, other planets, or inside the human body. Such experiences make the concepts that might sound abstract or hard to visualize much easier for learners to grasp.
AR is also becoming increasingly popular for such subjects that require heavy visual understanding. An AR app can show what used to be a simple diagram in the textbook as a rotating 3D model or an animated explanation. This aids those students who learn more effectively through hands-on means or visual learning, rather than pure text-based study.
Teachers often remark that these resources not only enhance levels of engagement but also make explaining concepts easier. Instead of pure lectures, educators can combine immersive content with more traditional materials to offer a deeper learning experience.
Transforming Modern Business Operations

Besides education, immersive technology is changing the way business is carried out. Many industries today use VR for training programs, especially in those fields where safety, precision, or practice by repetition is required. It helps manufacturing workers, surgeons, pilots, and engineers all rehearse their tasks in controlled virtual settings before performing them in real-world environments.
Meanwhile, Mixed Reality makes it easier for designing and engineering teams to collaborate. Instead of peering at flat drawings or computer screenshots, the teams project full-scale 3D models into a physical workspace. In this way, they can easily walk around the model, inspect the details, and make adjustments together. The process cuts development timelines and reduces costly design mistakes.
Even collaboration at a distance has gotten better: remote colleagues can enter a virtual room together, look together at prototypes, and interact with each other in ways more natural than screen-to-screen video calls.
Immersive Entertainment: The Future Ahead
Entertainment remains among the most dynamic sectors in which innovation concerning AR, VR, and MR happens. Virtual worlds that could transport players into environments they could walk through, react to, and study freely can be built for game developers. Beyond gaming, cultural events such as virtual concerts and virtual sightseeing are being made available to those who could not participate in them physically. Augmented reality overlays have become common during sports broadcasts to help viewers understand statistics, motion patterns, or tactical decisions. Such visual enhancement creates a more engaging experience without taking away from the live nature of the event.
Conclusion
AR, VR, and MR are no longer experimental technologies made for very niche communities. Instead, they have almost become essential tools that enhance creativity, communication, and problem-solving processes across education, business, and entertainment. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will create opportunities that go far beyond what is available today and make immersive digital experiences an increasingly natural part of everyday life.